AI-Powered Tumor Detection: A Game Changer in Neurosurgery
The latest breakthrough in artificial intelligence (AI) technology has been unveiled by a team led by Dr. Hervey Jumper and Dr. Todd C. Hollon from the University of Michigan’s Department of Neurosurgery. Published in the prestigious journal Nature, this innovative AI tool can detect tumor infiltration from fresh, unprocessed tissue samples within seconds, significantly outperforming conventional surgical adjuncts in detection of residual tumors.
How the AI Tool Works
The AI tool, developed by the team, leverages advanced machine learning algorithms to analyze tissue samples in real-time. This allows surgeons to identify and remove residual tumor tissues more accurately and efficiently than traditional methods. The tool’s ability to process unprocessed tissue samples rapidly is a significant advancement, providing real-time guidance during surgery and potentially improving patient outcomes.
Performance and Accuracy
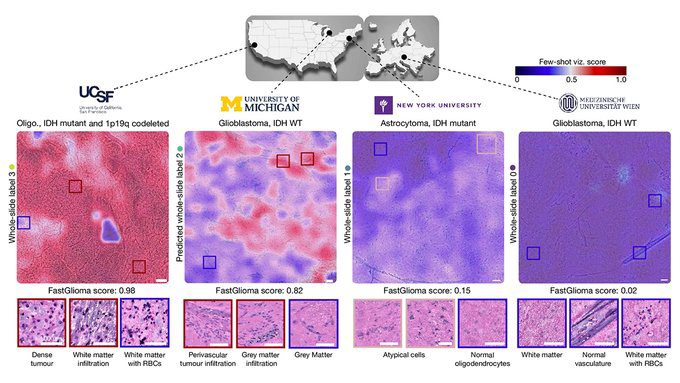
The AI tool has demonstrated remarkable accuracy in detecting residual brain tumors. According to the research, the AI model, named FastGlioma, has an average success rate of 92% in detecting residual tumors, compared to the 75% success rate of traditional methods. This significant improvement in accuracy can be attributed to the AI’s ability to analyze complex tissue patterns that are often missed by human eyes.
Comparison with Traditional Methods
Traditional methods for detecting residual tumors during surgery often involve the use of MRI and dyes, which can be time-consuming and less accurate. The FastGlioma AI tool, on the other hand, can analyze tissue samples in just 10 seconds, providing real-time feedback to surgeons. This rapid analysis not only saves valuable time during surgery but also reduces the risk of leaving behind residual tumor tissues.
Implications for Future Neurosurgery
The introduction of AI tools like FastGlioma marks a significant milestone in the field of neurosurgery. By providing surgeons with real-time, accurate information, these tools can enhance surgical precision and improve patient outcomes. The success of FastGlioma also paves the way for the development of similar AI tools for other types of cancer and medical conditions, further integrating AI into the healthcare sector.
Related Articles
- AlphaFold2: The AI Revolutionizing Protein Structure Prediction
- AI technology for breast cancer screening and AI tool may help better detect, treat cancers.
Related Articles
- AlphaFold2: The AI Revolutionizing Protein Structure Prediction
- Radiologist AI Teamwork Demonstrated for Report Generation via a Vision-Language Foundation Model
Looking for Travel Inspiration?
Explore Textify’s AI membership
Need a Chart? Explore the world’s largest Charts database