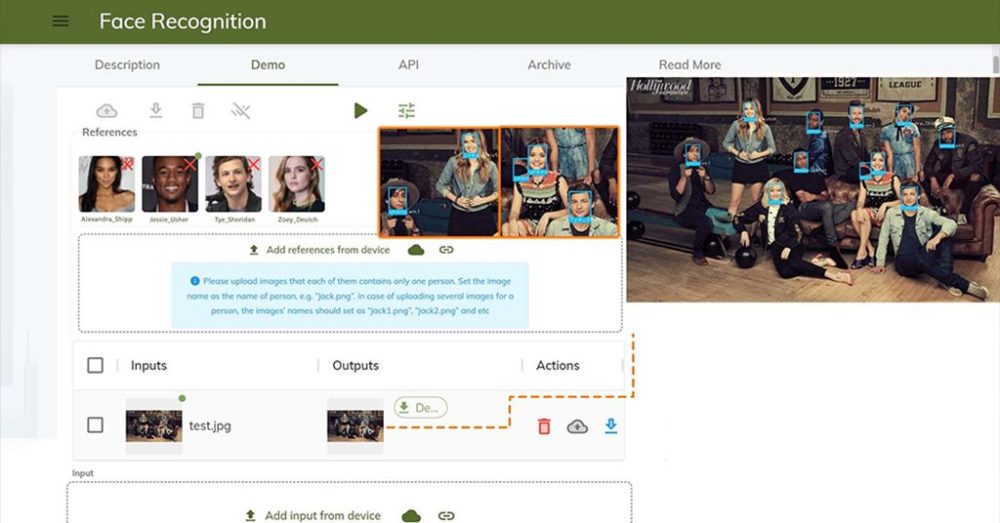
In today’s digital age, facial recognition technology is revolutionizing the banking industry by enhancing security, streamlining operations and personalizing the customer experience. As financial institutions seek more robust authentication methods, traditional passwords and PINs are no longer sufficient to protect sensitive data. Facial recognition leverages unique biometric identifiers to provide a secure, convenient alternative that minimizes the risk of unauthorized access and fraud.
As an AI company, Saiwa provides cutting-edge facial recognition services tailored for many industries, including the banking industry. Our technology not only strengthens security protocols, but also improves operational efficiency by automating customer authentication and access control. Saiwa’s facial recognition services seamlessly integrate with smart banking systems to deliver faster, more personalized interactions while maintaining the highest standards of privacy.
Importance of Face Recognition for Financial Institutions
Financial institutions have a fundamental responsibility to safeguard customer data and assets. Traditional authentication methods, such as passwords and PINs, are susceptible to breaches and unauthorized access. Face Recognition in Banking offers a more robust security measure by leveraging unique biometric identifiers inherent to an individual’s facial features. This technology can be integrated into various banking applications, bolstering security protocols and deterring fraudulent activities.
Beyond security, face recognition can improve operational efficiency and enhance customer service within banks. By automating authentication processes and enabling faster, more convenient access to accounts, face recognition technology can streamline banking interactions for both customers and staff.
Face Recognition Technology: Core Components
Face recognition technology operates through a series of distinct stages:
- Image acquisition
The initial step involves capturing a facial image using a camera or other imaging device. The quality of the captured image significantly impacts the accuracy of the subsequent recognition process. Factors like lighting conditions, pose variations, and camera resolution need to be considered for optimal image acquisition.
- Face detection
Once an image is captured, the system employs algorithms to locate and isolate the human face within the image frame. This initial step separates facial regions from the background and may involve techniques like edge detection or pattern recognition to identify facial features. This is crucial for applications like security systems or identity verification, where accuracy is paramount. Age verification also benefits from this, as it can prevent underage individuals from accessing age-restricted content or services.
Face Recognition Techniques
Several facial recognition techniques can be employed by banking systems:
- 2D face recognition
This is the most widely used technique, analyzing facial features like eyes, nose, mouth, and the overall geometry of the face within a two-dimensional image. Advanced algorithms extract distinct feature points and compare them against a database of stored facial templates. While computationally efficient, 2D recognition can be susceptible to variations in lighting, pose, and facial expressions.
- 3D face recognition
This technique captures the three-dimensional structure of a face using specialized cameras or depth sensors. By creating a digital 3D model of the face, this method offers greater resilience against variations in lighting and pose compared to 2D recognition. However, 3D technology is generally more expensive to implement and requires specialized hardware.
- Thermal face recognition
This technique utilizes thermal imaging cameras that capture heat signatures emitted by the face. This method is particularly advantageous in low-light conditions or scenarios where individuals attempt to disguise themselves with facial coverings. However, thermal face recognition systems can be more expensive than traditional cameras and may be less accurate in identifying individuals with similar facial structures.
The choice of face recognition technique depends on the specific security requirements and operational environment of a financial institution. Banks may employ a combination of techniques to achieve optimal accuracy and address potential limitations of individual methods.
What is Smart Banking?

Smart banking refers to the integration of technology into traditional banking services, offering customers convenient and secure access to their accounts through various digital channels. This encompasses mobile banking apps, online banking platforms, and self-service kiosks within bank branches. Smart banking solutions prioritize user-friendliness and provide a range of functionalities, including account management, bill payments, money transfers, and investment services.
Face Recognition in Banking Sector
The application of face recognition in banking falls under the umbrella of smart banking technologies. By integrating facial recognition into these systems, banks can leverage several functionalities:
Specific Applications of Face Recognition AI in Banking

Customer authentication for transactions
Face recognition AI can be used to securely authenticate customers for various banking transactions. This can be implemented for online banking logins, mobile app access, or authorizing transactions at ATMs and self-service kiosks. Compared to traditional passwords and PINs, which can be forgotten or compromised, facial recognition offers a more secure and convenient authentication method.
Fraud detection and prevention
Facial recognition AI systems can be employed to detect and prevent fraudulent activities. When a customer attempts to access an account or conduct a transaction, the system can compare their live facial image against a database of authorized users. This can deter unauthorized access attempts and alert bank personnel to potentially fraudulent activity. Deepfake Detection API can further enhance security by identifying manipulated media content in customer verification processes, ensuring data authenticity and preventing sophisticated fraud attempts.
Access control for employees and restricted areas
Within bank branches, face recognition can be used to control access to restricted areas like server rooms or secure vaults. This ensures only authorized personnel can enter sensitive areas, safeguarding valuable assets and confidential information.
Personalized customer service
Facial recognition AI can be used to personalize customer service interactions. Banks can identify returning customers and tailor their service offerings based on individual banking habits and preferences. This can create a more engaging and efficient customer experience.
Benefits of Facial Recognition System in Banking
Facial recognition in banking offers significant advantages. It strengthens security by replacing passwords with unique biometric identifiers. This deters unauthorized access and fraud. Additionally, facial recognition streamlines operations by automating authentication, reducing wait times and improving customer satisfaction. Furthermore, this convenient and contactless method eliminates the need for remembering passwords or carrying multiple cards. Overall, facial recognition technology enhances security, reduces costs, and creates a more positive customer experience within the banking sector.
Conclusion
Face recognition AI technology presents a transformative opportunity for the banking sector.
Face Recognition in Banking has the potential to revolutionize the industry by bolstering security, optimizing operations, and enhancing customer experiences. However, addressing its challenges and limitations is crucial for banks. Ensuring stringent data security measures, addressing privacy concerns, and deploying the technology ethically are imperative for its successful integration into the banking landscape. As Face Recognition in Banking evolves and matures, overcoming current limitations, it stands poised to become a cornerstone of secure and efficient smart banking solutions in the future.
Check out more AI tool.
Elevate Guest Experience with RoomGenie
Research latest trends effortlessly 🚀 Check out NewsGenie