If you are learning machine learning or data science, you will often encounter datasets with hundreds or even thousands of features. This is where PCA in machine learning becomes essential.
This guide explains what PCA is, why it is used, and how it works, in plain English first, followed by technical clarity—without unnecessary math overload.
Related Blogs:
What Is PCA in Machine Learning?
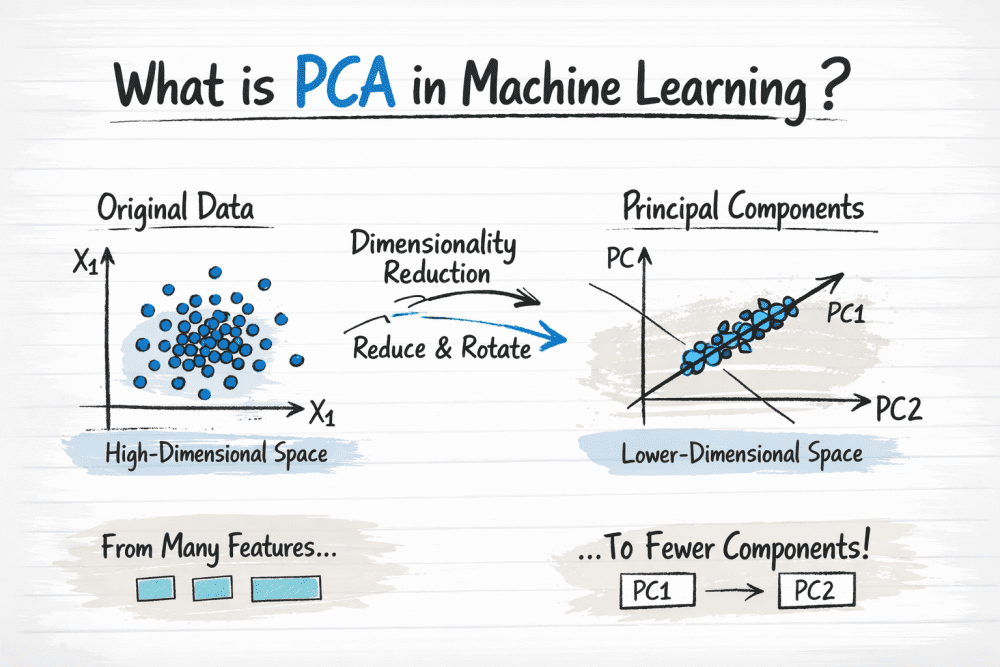
Principal Component Analysis (PCA) is an unsupervised learning technique used for dimensionality reduction.
It transforms high-dimensional data into a smaller number of meaningful variables (called principal components) while preserving as much information (variance) as possible.
In simple terms:
- PCA reduces the number of features
- Keeps important patterns
- Removes redundancy and noise
This makes machine learning models faster, more stable, and easier to visualize.
Why Do We Need PCA? (The Curse of Dimensionality)
As the number of features increases:
- Data becomes sparse
- Models become slow
- Risk of overfitting increases
- Distance-based algorithms (KNN, clustering) perform poorly
This phenomenon is called the curse of dimensionality.
How PCA Helps
- Removes correlated features
- Compresses information into fewer dimensions
- Improves generalization and performance
How PCA Works: A Step-by-Step Breakdown

PCA follows a systematic mathematical process, but the intuition is simple:
– Find new axes that capture the maximum variance in the data.
Step 1: Data Standardization (Why It’s Non-Negotiable)

PCA is scale-sensitive.
If one feature ranges from 0–1000 and another from 0–1, PCA will be biased.
✔ Standardization ensures:
- Mean = 0
- Standard deviation = 1
- Fair contribution from all features
Step 2: Covariance Matrix Computation

The covariance matrix shows how features vary together.
- High covariance → strong relationship
- PCA identifies directions of maximum covariance
This is how PCA detects redundant information.
Step 3: Calculating Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors

- Eigenvectors → directions (principal components)
- Eigenvalues → importance of each direction
PCA:
- Sorts eigenvalues (highest to lowest)
- Selects top components
- Discards low-variance directions
Result: compressed but information-rich data
Key Benefits of Using PCA

Overfitting Reduction & Performance Boost
- Fewer features = simpler models
- Reduced noise = better generalization
Data Visualization (Turning 10D into 2D)
- Visualize clusters and patterns
- Ideal for exploratory data analysis
Storage & Computation Efficiency
- Smaller datasets
- Faster training and inference
PCA vs LDA: What’s the Difference?

| Aspect | PCA | LDA |
|---|---|---|
| Learning Type | Unsupervised | Supervised |
| Uses Labels | ❌ No | ✅ Yes |
| Objective | Maximize variance | Maximize class separation |
| Common Use | Feature reduction | Classification tasks |
Rule of thumb:
- Use PCA when labels are unavailable
- Use LDA when class separation is critical
Implementation: PCA in Python with Scikit-Learn
from sklearn.decomposition import PCA
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
# Standardize data
scaler = StandardScaler()
X_scaled = scaler.fit_transform(X)
# Apply PCA
pca = PCA(n_components=2)
X_pca = pca.fit_transform(X_scaled)
print(pca.explained_variance_ratio_)
✔ Widely used in pipelines
✔ Integrates seamlessly with ML models
✔ Supports variance-based component selection
Modern Use Cases of PCA (2026 Perspective)
PCA is still highly relevant today:
- LLM embeddings compression
- Preprocessing before clustering
- Noise reduction in sensor data
- Visualization of high-dimensional AI representations
Even with deep learning, PCA remains a foundational tool.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
When should I use PCA in machine learning?
Use PCA when:
- You have many correlated features
- Training time is high
- Visualization is difficult
Does PCA reduce accuracy?
Not necessarily.
In many cases, PCA improves accuracy by removing noise and redundancy.
Is PCA a feature selection technique?
No. PCA is feature extraction, not selection—it creates new features.
Final Thoughts
Understanding what PCA is in machine learning is crucial for anyone working with real-world data. PCA helps you simplify complexity, improve performance, and gain insights from high-dimensional datasets—without losing what truly matters.
If you’re building robust ML systems in 2026, PCA is not optional—it’s foundational.